https://sputniknews.in/20240301/indian-scientists-innovate-eco-friendly-wound-dressing-using-banana-fibres-6713889.html
Indian Scientists Innovate Eco-Friendly Wound Dressing Using Banana Fibres
Indian Scientists Innovate Eco-Friendly Wound Dressing Using Banana Fibres
Sputnik India
India, the largest banana-farming country, can use discarded banana pseudo stems to create banana fibres dressing, providing sustainable wound care and minimizing environmental harm.
2024-03-01T19:13+0530
2024-03-01T19:13+0530
2024-03-01T19:13+0530
science & tech
india
science & tech
health
environment
environmental crisis
health crisis
health issues
healthcare system
investigation
https://cdn1.img.sputniknews.in/img/07e8/03/01/6715124_0:11:576:335_1920x0_80_0_0_24838b4ecef58d7bc0b97b73848d4f38.jpg
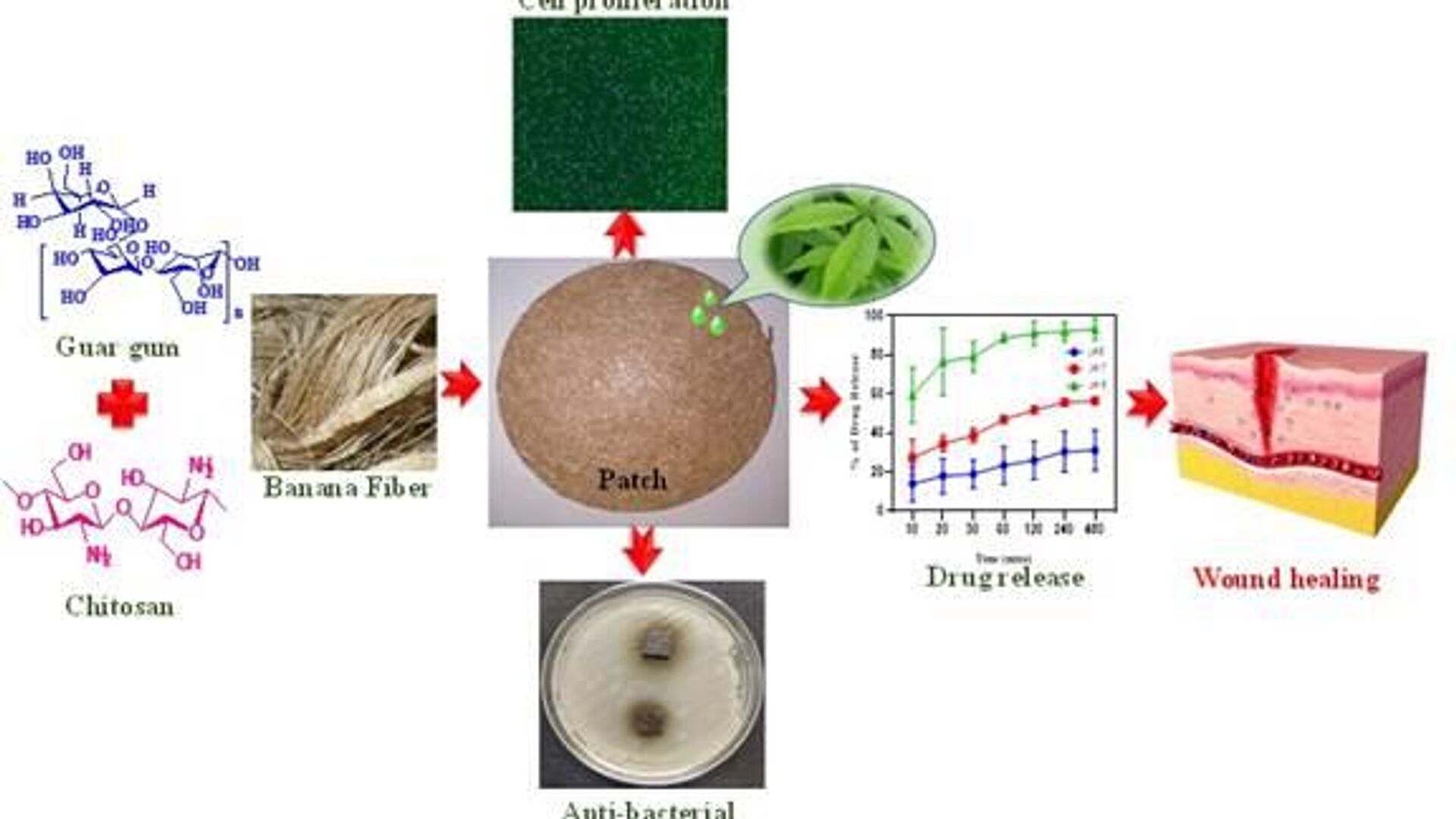
Researchers at the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) have achieved a significant breakthrough by developing a new method of converting banana pseudo-stems, which are typically discarded as agricultural waste, into a sustainable material for wound dressings. The study, published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, describes how a combination of banana fibres, chitosan and guar gum (or guaran) was successfully used to create a versatile dressing with remarkable mechanical strength and antioxidant properties.Professor Devasish Chowdhury, the lead researcher on the project, emphasised that this innovative approach represents a significant milestone in the field of wound healing. He further stated that this discovery, which offers a cost-effective, non-toxic, and environmentally friendly alternative, has the potential to revolutionize biomedical research.
https://sputniknews.in/20231226/electrifying-hydroponics-scientists-make-barley-grow-50-faster-5969570.html
india
Sputnik India
feedback.hindi@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
2024
Sangeeta Yadav
https://cdn1.img.sputniknews.in/img/07e6/0c/0f/110602_0:0:641:640_100x100_80_0_0_c298016a79eb02ef8caa9d1f688c12a5.jpg
Sangeeta Yadav
https://cdn1.img.sputniknews.in/img/07e6/0c/0f/110602_0:0:641:640_100x100_80_0_0_c298016a79eb02ef8caa9d1f688c12a5.jpg
News
en_IN
Sputnik India
feedback.hindi@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Sputnik India
feedback.hindi@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Sangeeta Yadav
https://cdn1.img.sputniknews.in/img/07e6/0c/0f/110602_0:0:641:640_100x100_80_0_0_c298016a79eb02ef8caa9d1f688c12a5.jpg
largest banana-farming country, banana pseudo stem, wound care, environmental harm, scientist, institute of advanced study in science and technology (iasst), banana pseudo stems, agricultural waste, environmentally friendly material, wound dressing, study published in, international journal of biological macromolecules, banana fibers, antioxidant, cost-effective, non-toxic, prof. devasish chowdhury, biomedical research
largest banana-farming country, banana pseudo stem, wound care, environmental harm, scientist, institute of advanced study in science and technology (iasst), banana pseudo stems, agricultural waste, environmentally friendly material, wound dressing, study published in, international journal of biological macromolecules, banana fibers, antioxidant, cost-effective, non-toxic, prof. devasish chowdhury, biomedical research
Indian Scientists Innovate Eco-Friendly Wound Dressing Using Banana Fibres
India, the largest banana growing country, can use discarded banana pseudo-stems to make banana fiber dressings, providing sustainable wound care and minimizing environmental impact.
Researchers at the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) have achieved a significant breakthrough by developing a new method of converting banana pseudo-stems, which are typically discarded as agricultural waste, into a sustainable material for wound dressings.
The study, published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, describes how a combination of banana fibres, chitosan and guar gum (or guaran) was successfully used to create a versatile dressing with remarkable mechanical strength and antioxidant properties.
Professor Devasish Chowdhury, the lead researcher on the project, emphasised that this innovative approach represents a significant milestone in the field of wound healing.
He further stated that this discovery, which offers a cost-effective, non-toxic, and environmentally friendly alternative, has the potential to revolutionize biomedical research.